|
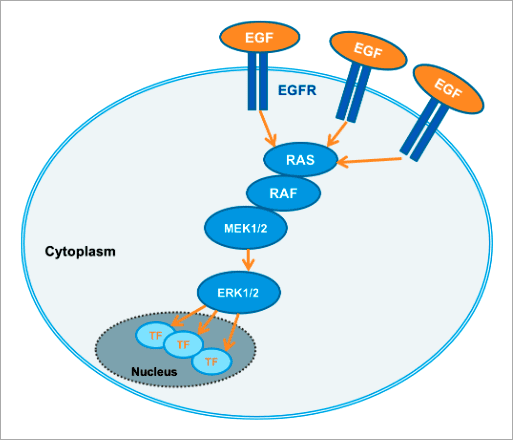
✨ 高内涵影像分析應用實例 以 FRET 生物感測器分析活細胞內 細胞外訊息調節蛋白激酶 ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinase) 是胚胎發育、細胞分化、細胞增殖和細胞死亡的關鍵調控因子 [1]。ERK 訊息傳導路徑起源於細胞膜表面受體 (Receptor) 的活化,並經由細胞內 RAS、RAF、MEK 等蛋白激酶將訊息傳遞給 ERK(圖 1)。ERK 途徑可經由不同型式的受體激活,包含屬於受體酪氨酸激酶 (Receptor tyrosine kinases, RTKs) 家族的 EGF 受體 (EGF receptor, EGFR) 以及 G 蛋白耦合受體 (G protein-coupled receptors, GPCRs) [2]。ERK 身為此途徑的最終成員,會作用在細胞內許多不同的蛋白質上使其磷酸化,包含多種激酶與轉錄因子。在許多類型的癌症中都能觀察到 ERK 訊息傳導路徑的變異,因此被視為是干預性治療的熱門研究標的 [3]。
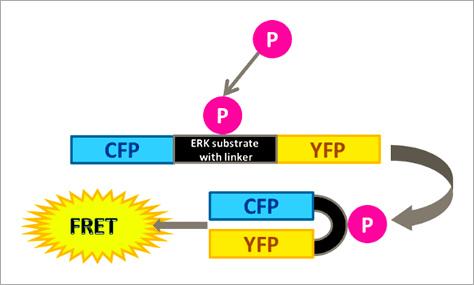
Figure 1. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling cascade propagates signals from cell surface receptors such as the EGF receptor (EGFR) to intracellular proteins. ERK is the final component of this pathway and upon activation by growth factors, such as EGF (epidermal growth factor), downstream effects, for example, activation of kinases or transcription factors, are triggered. 本文闡述如何透過福斯特共振能量轉移 (Förster resonance energy transfer, FRET) 效應原理所設計出的 ERK 生物感測器,搭配 Operetta CLS™ 高內涵影像系統進行自動化的活細胞 ERK 訊息傳導路徑分析,並應用於 ERK 途徑調節藥物的開發。 基於 FRET 原理構築的 ERK 生物感測器 FRET 是非放射性能量從能量捐贈分子 (Donor molecule) 傳遞至能量接受分子 (Acceptor molecule) 的一種能量轉移現象,此現象僅會在兩者距離小於 10 nm 時才會產生,因此可作為研究分子鄰近度變化的靈敏工具,例如蛋白質交互交用(研究兩個分子彼此之間的距離,Interamolecular FRET)、或蛋白質構形變化(研究分子內部構造之間的距離,Intramolecular FRET)[4, 5, 6]。 在此次的 ERK 訊息傳導路徑研究中,我們使用的策略為「Intramolecular FRET」,採用稱為 EKAREV (ERK activity reporter with Evee backbone) 的生物感測器。穩定表現該生物感測器的細胞株則由 Somponnat Sampattavanich 教授友情提供。 EKAREV 生物感測器是用基因重組技術所架構的單一融合蛋白 (Fusion protein),能量捐贈分子「CFP 螢光蛋白」與能量接受分子「YFP 螢光蛋白」之間間隔著一段 ERK 磷酸化作用受質序列。當此受質區域被 ERK 磷酸化後,由於構形的變化,使得 CFP 螢光蛋白能夠接近 YFP 螢光蛋白,進而產生能量轉移,最終產生 515-580 nm 的 FRET 螢光訊號(圖 2)。EKAREV 生物感測器在設計時已通過層層優化,確保能夠降低偶發性 FRET 螢光背景值,並使其能夠靈敏地隨著 CFP 與 YFP 螢光蛋白之間距離的拉近,產生可靠的正相關訊號 [7, 8]。
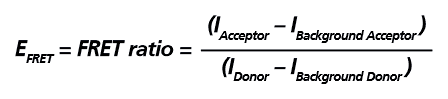
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity reporter (EKAREV). In this biosensor, the two fluorescent proteins are separated by an ERK substrate domain, a linker, and a binding domain. Once the ERK substrate domain undergoes phosphorylation by ERK, a conformational change is triggered bringing CFP and YFP into close proximity and allowing FRET to occur. EKAREV 生物感測器可作為「Intramolecular FRET」的典型範例,在 EKAREV 生物感測器中能量捐贈分子與能量接受分子以 1:1 的比例存在,因此僅需偵測能量捐贈分子與能量接受分子的發射螢光訊號,並扣除其各自的背景螢光進行校正,即可計算出該實驗的相對 FRET 效率 (EFRET),其計算公式如下圖所示。
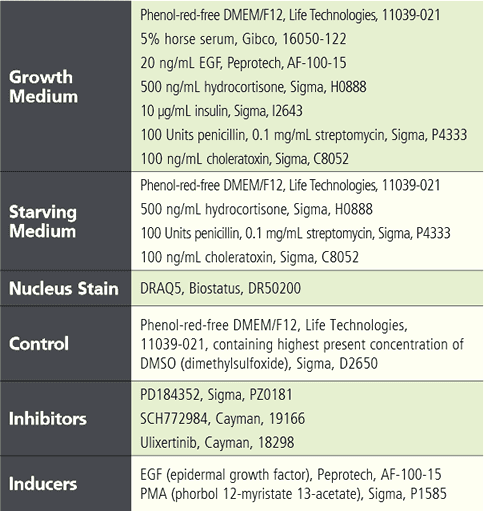
實驗流程與材料 將表現有 EKAREV 生物感測器的穩定細胞株以 1.2 x 10^4 cells / 150 μL / well 的量接種至 96 孔盤中 (PhenoPlate)。經過兩天的培養,以 150 μL 血清飢餓培養基沖洗細胞兩次後,將細胞置於飢餓條件下培養五小時以降低細胞內基礎 ERK 活性。在飢餓培養起始階段,加入不同濃度的抑制劑 (Inhibitor) 或 DMSO 與細胞共同培養,並在培養四個半小時後以 DRAQ5 螢光染劑進行細胞核染色。接著再次以飢餓培養基沖洗細胞一次後,重新加入含有 8 μL 二十倍濃縮抑制劑或 DMSO 對照的 150 μL 新鮮飢餓培養基。作為參考,在某一時間點加入 8 μL 二十倍濃縮誘導劑 (Inducer)。在此實驗中,使用含有或不含有測試藥劑之血清飢餓培養基(內含最高濃度的 DMSO)作為對照組。詳細實驗材料請見下表說明。
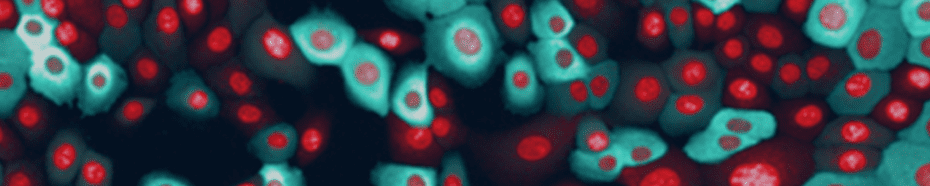
Tabel 1. List of assay reagents, compounds and media. 高內涵細胞影像擷取 使用 Operetta CLS 系統,於寬域 (Widefield) 模式下以 20 倍高 NA 物鏡 (NA 0.8) 掃描擷取細胞影像, 獲取圖像時間總長 97 分鐘。將 FRET 誘導劑添加至血清飢餓細胞後,每 8 分鐘擷取一次影像,並針對實驗所使用到的螢光分子設置四個偵測渠道,分別是:DRAQ5 (Ex 615-645 nm / Em 655-760 nm)、CFP (Ex 435- 460 nm / Em 470-515 nm)、YFP (Ex 490-515 nm / Em 525-580 nm) 和 FRET (Ex 435-460 nm / Em 515-580 nm)(圖 3)。
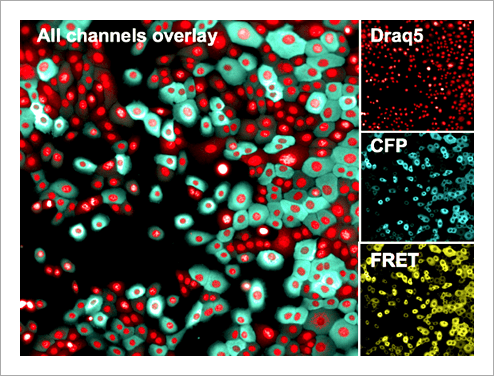
Figure 3. Human mammary epithelial cells stably expressing the EKAREV biosensor. Nuclei were stained with DRAQ5. Subsequently, cells were imaged using a 20x high NA objective in widefield mode on the Operetta CLS system. Although this is a stable cell line, note the relatively inhomogeneous expression levels of the biosensor. 影像分析 使用 Harmony® 高內涵影像分析軟體進行擷取影像的自動化分析。簡單來說,影像會被分割界定為細胞或背景。能量捐贈分子與反應所產生的 FRET 螢光訊號,會分別在細胞質與背景中進行偵測與計算,然後以經過背景校正的 FRET 比率作為最終結果(圖 4)。
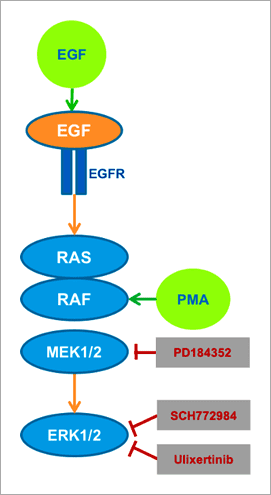
Figure 4. Image analysis workflow for ratiometric FRET quantification using Harmony software: cytoplasm of cells and background are segmented and low-expressing cells excluded by an intensity threshold. Intensity of donor and FRET channels and their appropriate backgrounds are quantified and the background-corrected FRET intensity ratio calculated. Subtracting background intensities is especially advantageous in live-cell applications where media with autofluorescent components often result in higher backgrounds and thus smaller assay windows. 實驗結果 為了探究是否真的可以使用 FRET 原理設計出的生物感測器,搭配 Operetta CLS™ 高內涵影像系統進行 ERK 訊息傳導路徑調節因子的研究,我們使用不同的 ERK 與 MEK 活化劑 (Activator) 及抑制劑處理 EKAREV 生物感測器表現細胞(圖 5)。PMA 和 EGF 可視為是 RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK 這個訊息傳導途徑的專一性活化劑,EGF 會專一性地與細胞膜表面的 EGF 受體「EGFR」結合,而 PMA 則因為具有親脂性,可直接穿透細胞膜,進入細胞內活化 RAF。抑制劑部分,PD184352 會針對 MEK1/2 進行抑制,而 Ulixertinib 與 SCH772984 則可有效抑制 ERK1/2。
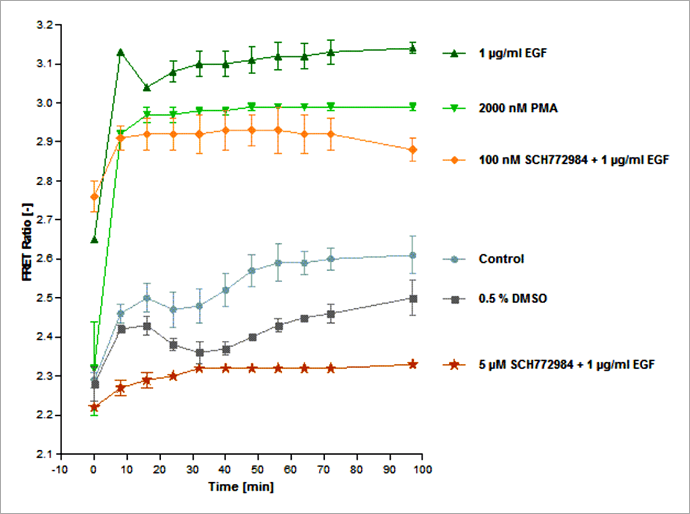
Figure 5. Schematic overview of exogenously added activators (green) and inhibitors (red) and their impact on the ERK signaling pathway. The EKAREV-expressing cells were treated with EGF or PMA to induce ERK activation, or, in addition, with one of three MEK and ERK-specific inhibitors (PD184352, SCH772984, Ulixertinib), interrupting signal transduction at different positions of the pathway. 首先,為了更多瞭解 FRET 生物感測器在藥物處理後所產生的變化,我們進行了長達 97 分鐘的紀錄實驗。如同我們所預期的,與未處理藥物的細胞相比,加入 EGF 或 PMA 的確可以導致細胞的 FRET 比率強烈增加(圖 6),並約在 30 分鐘後進入訊號高原期。而未處理藥物的對照組細胞,則是表現出較低的 ERK 活性,然而仍可觀察到 FRET 比率隨著時間穩定緩慢地上升,推測這是因為 ERK1/2 能被多種生長因子與有絲分裂所調控,因此在活細胞影像分析實驗過程中,ERK 受到自分泌 (Autocrine) 或旁分泌 (Paracrine) 信號所活化。同時使用 ERK 抑制劑「SCH772984」與 EGF 處理細胞,可發現隨著抑制劑劑量的增加,FRET 比率也隨之下降。在 5 μM SCH772984 藥物處理下,由 EGF 所引發的 ERK 活化幾乎可以忽略不計,這表示在此藥物劑量下 ERK 活性受到完全抑制。值得注意的是,此次實驗所使用到的 DMSO 最高濃度為 0.5%,的確會對實驗結果產生影響造成 FRET 比率降低,因此需要額外加入 0.5% DEMSO 這一組對照組。另一個 ERK1/2 抑制劑「Ulixertinib」的實驗結果與 SCH772984 類似(數據並未呈現於本文中)。
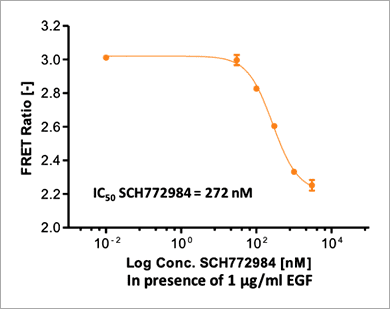
Figure 6. Time course of ERK signaling measured with the EKAREV FRET-based biosensor on the Operetta CLS system. Stimulation of ERK via EGF or PMA induces a rapid FRET signal increase that plateaus after about 30 min. High concentrations of SCH772984 (5 μM) lead to almost complete inhibition of ERK activation (in presence of 1 μg/mL EGF) as almost no FRET signal increase is measurable. Higher dilutions of SCH772984 only partially inhibit the EGF-induced ERK activation. The control curve shows an intermediate, slightly rising FRET signal without any treatment. FRET signals are slightly inhibited by 0.5 % DMSO, which was the highest concentration of DMSO used in the experiment. Assay statistics: Z`= 0.87 (as calculated at time point 32 min, DMSO being the negative and EGF the positive control). 因為 FRET 訊號在 32 分鐘時達到穩定期,因此我們選擇這個時間點進行 SCH772984 的 IC50 值檢測。使用 1 μg/mL EGF 與六個序列稀釋濃度(濃度範圍 10 pM 至 3 μM)的 SCH772984 抑制劑處理 EKAREV 生物感測器表現細胞。實驗結果顯示,SCH772984 的 IC50 值為 272 nM(圖 7)。
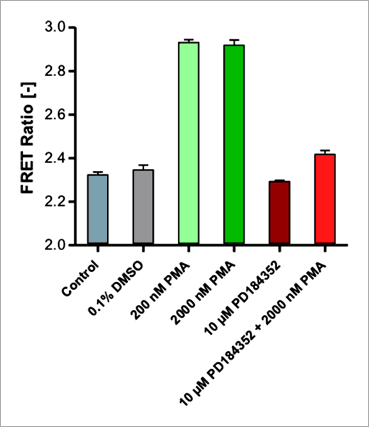
Figure 7. The ERK inhibitor SCH772984 leads to a dose-dependent decrease of FRET-based EKAREV signals. EKAREV cells were treated with increasing concentrations of SCH772984 in the presence of 1 μg/mL EGF. The FRET ratio was determined on the Operetta CLS system after 32 min of incubation, as signals stabilized at this time point. The high Z’ value (Z’ = 0.89) shows an excellent assay performance. 此外,為了進一步確認本偵測平台是否可以應用於研究直接作用在 MEK1/2 的 ERK 途徑調節因子,我們使用 MEK1/2 抑制劑「PD184352」來測試施以 PMA 藥物活化的 EKAREV 生物感測器表現細胞。實驗結果顯示,本偵測平台的確可以檢測到 PD184352 對 PMA 所引發的 ERK 活化具有抑制效果(圖 8)。
Figure 8. Inhibition of the PMA activated RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling cascade by PD184352 measured on the Operetta CLS system. EKAREV cells were treated with an alternative set of activator and inhibitor (PMA + PD184352) acting further upstream on RAF/MEK (compare with Figure 5). EKAREV cells treated with either 200 or 2000 nM PMA show a high FRET response (32 min post induction). The activation is inhibited by co-incubating the cells with the MEK1/2 specific inhibitor PD184352 at a concentration of 10 μM. 結語 透過本文,我們證實 EKAREV FRET 生物感測器與 Operetta CLS™ 高內涵影像系統的結合,可以用來進行 ERK 訊息傳導路徑調節因子的活細胞檢測與分析。藉由此平台,我們可以鑑別找尋 RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK 訊息傳導路徑的可能作用新藥,並且由於實驗是以活細胞型式進行,因此相較於一般 ERK 磷酸化生化檢測反應僅能進行終點訊號偵測,此平台更能真實反應藥物在細胞中對於訊息傳導路徑的動態影響。儘管 EKAREV 生物感測器表現細胞群中存在有生物感測器表現量不一致的問題(圖 3),但以 FRET 比率呈現的數據顯示方式,提供了極佳的分析數據和統計意義,Z' 值高於 0.87。 EKAREV 生物感測器的優質設計、以及 Operetta CLS™ 高內涵影像系統的優越成像品質、加乘上 Harmony® 高效精準的影像分析運算能力,皆有助於提升高内涵 FRET 分析平台的穩定性。Harmony® 影像分析軟體的建構區塊概念,允許創建易於設置和理解的圖像分析序列,並且不需要專業的影像分析知識。 相較於使用傳統顯微鏡的檢測實驗,本平台結合了 FRET 生物感測器與高內涵影像系統,不僅能夠提供更豐富的檢測資訊、並且提高了實驗通量,為細胞訊息傳導的基礎研究和藥物開發開闢了新的可能性。更多應用知識與詳細產品資訊,歡迎洽詢 Revvity 台灣代理 — 伯森生技。 References
|
|

|